Product » A free email server for Windows and Linux » Features available in Xeams
AI-Powered Junk Mail Filtering
- AI-Powered Junk/Spam filtering.
- Checks SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
- IP based filters that check the reputation of the sender's IP
- Checked for viruses in attachment
- Content filtering based on user defined rules as well as Bayesian analysis
- Attachment filtering
- Company policy rules
- Finger print analysis
- and more...
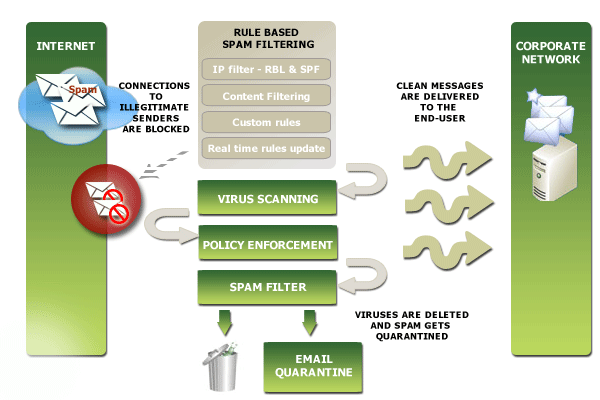
Feature details
Xeams uses a sophisticated score based mechanism to decide if an email should be considered junk. Every incoming and out-going email is assigned a score. Based on this score, Xeams assigns one of three categories to the email:
- Junk
- Possible Junk
- Good
Besides Junk and Good, Xeams utilizes a third category called Possible Junk. Occasionally, if an email to too close to being good or junk, it is assigned this category, providing the users to manually decide if they want to mark them as junk or good. By default if an email gets a score less than 60, it is considered good. A score of 100 or higher is considered junk. Score between 60 and 100 is considered Possible Junk.
Scoring criteria
Scoring is done based on several built-in rules. Every rule in the system can take the score either in the positive or negative direction. The final score decides the category of the email. Rules in Xeams can be further divided into two categories:
- User defined rules
- Self-learning rules
Self-learning rules adapt to the environment of your users. For example, it learns from the past history of emails to assign a score to future emails. One such rule is called Bayesian Analysis. Another example of self-learning rule is when a local user sends a message to someone outside the network. Xeams remembers who the recipient is and gives credit to that user if he/she sends a reply back.
Score reasoning
Many spam filtering solutions block messages without giving an adequate reason of why it was selected as junk. Xeams, on the other hand, gives a detail description of why a particular email is considered junk. This description is very useful for administrators who want to fine tune the filtering rules.Types of rules in Xeams for email filtering
AI-Powered Filtering | |
|---|---|
| AI-Powered Filtering | AI-based email junk filtering provides improved accuracy and adaptability, enabling it to catch sophisticated threats and offer greater security against spam, phishing, and malware. It enhances productivity by reducing manual effort and email clutter. Using artificial intelligence, Xeams continuously evolves by learning from user behavior, attack trends, and cross-tenant intelligence. It detects never-before-seen threats without relying on static rules or signatures, and requires no manual tuning, rule writing, or policy maintenance. |
Custom filters | |
| Custom Filters | Custom filters are the most powerful and effective filters used in Xeams to detect junk messages. Often spammers use several tricks to avoid being filtered. These custom filters are specially designed to detect such tricks. We believe that these custom filters are so effective that leaving just these filters on you can eliminate 90% of all junk messages. |
IP/Domain Based Rules | |
| RBL | The word "RBL" stands for Real-Time Blackhole List. It refers to several services on the Internet that keep a database of IP addresses belonging to known spammers, virus sources and other exploits. Xeams queries these servers to check if the IP address exists in such a list. |
| SPF Check | The word "SPF" stands for Sender Policy Framework. SPF records are used to prevent email forgery on the Internet. Many companies publish their SPF data through their DNS server, which includes a list of IP addresses where an email can originate. Xeams tries to match the SPF record for incoming messages and assigns a score if a mismatch is found. |
| DKIM Check | Sender's domain name is checked for forgery using the DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). |
| DMARC | Incoming emails are checked for DMARC alignment, which is based on sender's domain rather than the IP address. |
| Black/White listing | Administrators can either black list or white list IP addresses in Xeams. A black listed IP address is assigned a positive score, whereas a white list IP address is assigned a negative score. |
Content Filters | |
| Finger print analysis | Xeams uses a proprietary method of creating a finger print of every email. This finger print is then compared with future messages to determine if it is part of a bulk-mail campaign. |
| Image analysis | Embedded images in emails are analyzed for patterns. |
| Body and Header | Xeams utilizes a two-pass approach to analyze the body of every message. It then compares it
with a known list of keywords containing a score. Rules can be specified for the following sections:
|
| Anti-Virus | There are three types of virus detection in Xeams
|
| Adaptive Filters | Adaptive filters are self-learning filters that gets smarter by analyzing the patterns of
previously sent and received emails. These filters include:
|
| Challenge Response | Challenge response is a mechanism where the system sends a challenge email to the sender to verify if it is a valid message. This type of filter is disabled by default but can be enabled if the users want to use it. |
