What Are The Different Types of End-to-End Email Encryption?
Electronic mail has been around since 1978 and is being used by billions of users on a daily basis. Privacy was not a big concern when it was introduced, and therefore, it lacks the essential security features necessary for private communication.
Several attempts have been made to address privacy between the sender and recipient, but there is no standardized way to solve this problem. Companies are increasingly looking for an easier way to ensure email security and privacy.
Email encryption is one of the most widely used methods to keep email communications private and secure.

The email encryption market is expected to grow to $11.8 billion by 2026 at a compound annual growth rate of 23.1%. This rapid growth in the email encryption industry is an indicator of companies worldwide realizing the need for encrypted and secure email solutions.
There are several types of email encryption solutions in the market, making it harder to pick the right one for your business. How do you select which one is best for your company?
This article talks about three different types of solutions that can be used to achieve secure and encrypted emails. It compares these models with each other in terms of their design and ease of use.
What is End-To-End Email Encryption?
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) aims to ensure no one but the intended recipient can see the message. In other words, for an end to end email encryption to be successfully implemented, the following must be true:
- Encryption must be performed as soon as the sender composes an email.
- This email stays in encrypted form until the recipient gets it.
- No one should be able to view or modify the message or attachments inside the email.

Emails typically go through several SMTP servers before reaching their final destination. TLS protects communication between servers. However, once it reaches the next hop, any administrator with access to the SMTP server can view and modify the message.
End-To-End Email Encryption prevents such modifications and guarantees that no intermediate software or an individual with access to the server can view or modify the message inside the emails.
What Is Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Is That Enough?
TLS stands for transport layer security, and as the name suggests, it only protects in-transit data. When you compose an email in MS Outlook, for example, the data typically goes through several routers and firewalls before reaching your company's SMTP server.
TLS guarantees a firewall or a network sniffer will not be able to peek inside the message. However, TLS cannot prevent the SMTP server from modifying the message. Employees in your company with access to the SMTP server could also look inside the messages you have sent to someone else.
Therefore, this method does not guarantee privacy once the email has reached an SMTP server. Only end-to-end email encryption can solve this problem.
So let's look at what are the different types of E2EE and how do they work.
Types of End-To-End Encryptions
End-to-End Encryption can be achieved by several methods, as described below.
- Both sender and recipient create a pair of public/private keys.
- Encryption is performed by applying mathematical operations to the actual data along with either public or private keys.
- If a message is encrypted with a public key, it can only be decrypted by a private key. On the flip side, a message encrypted with a private key can only be decrypted using the associated public key.
Steps To Encrypt
- The sender's email client encrypts the email using the public key of the recipient.
- Once the email is encrypted, PGP ensures that it can only be decrypted with the recipient's private key.
- On the receiving end, this encrypted email is finally decrypted by the recipient using his own private key.
Point to Note
The sender will need recipient's public key before encryption is performed.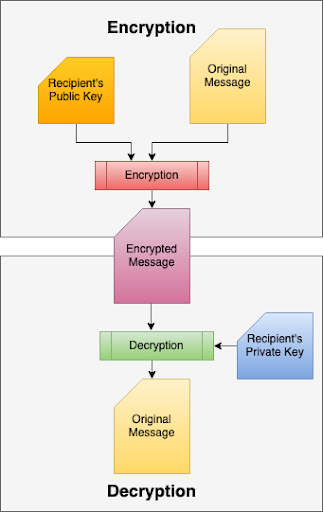
Advantages of using PGP
- Proven technology - PGP has been in use since 1991, and many email clients support it.
- Secure - Ensures no one but the intended recipient can view the message inside the email. It is a widely recognized encryption mechanism in the industry.
- Attachments - Entire email gets encrypted, including attachments.
Disadvantages of using PGP
- Usability - A novice user has no idea how to generate a public/private key. Many don?t even know what a public/private pair key is.
- Key Exchange - Public keys must be sent to both ends before encryption or decryption occurs. In other words, the sender will need the recipient?s public key and vice-versa. There are several ways to do that, and the users will have to get familiarized with them, adding minor hiccups.
- Software Plugin - PGP is typically enforced by the email client software used to compose the email. It is common for users to use a combination of mobile devices, laptops, desktops, and web-based email clients. It is a hassle to install these key pairs in every client the user intends to use. Additionally, these clients will have to support PGP, which may not be possible, particularly in web-based email systems.
Final Thoughts on PGP
Although PGP is a secure method for enabling end-to-end encryption for emails, it never got tracking in the mainstream because of the complexity, and run-around users have to go through before making it work.Steps To Encrypt
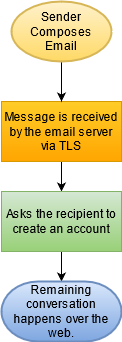
- The sender composes an email, which goes to the email server using TLS.
- Instead of sending the original message, the system asks the recipient notifying them about a private message and prompts them to create an account on the sender?s email system using HTTPS.
- Once the account has been created, the remaining communication occurs over the web.
- Optionally, email alerts are sent to the sender and recipient when the other party posts a reply.
Advantages of Using Email-to-HTTPS
- Usability - Easier to implement from the sender?s perspective.
- Any Client - No restriction on the email client. It can be used on mobile devices, laptops, desktops as well as web-based solutions.
- Attachments - Entire email gets encrypted, including attachments.
Disadvantages of Using Email-to-HTTPS
- More work for the recipient - Puts a burden on the recipient to create an account and remember passwords.
- Security - Less secure if an administrator on the receiving end intercepts the first message and creates an account before the intended recipient gets a chance.
- Transformation - It is no longer an email. Instead, it becomes a chat conversation on a website.
- Internet Required - Messages cannot be viewed if Internet access is not available.
Steps To Encrypt
- The sender composes an email using any client.
- The server receives this email over TLS.
- The email server converts the message into a password-protected PDF file, which is then attached to a generic message and is sent to the recipient.
- The recipient will only be able to view the message if he/she knows the password.

Advantages of Using Email-To-PDF
- Usability - Easy to use for both sender and recipient.
- Any client - Both sender and recipient could use any client on any device.
- Attachments - Entire message gets encrypted, including attachments. A PDF file can hold embedded attached files.
- No Internet Required - The Internet is not required once a message is downloaded locally.
Disadvantages of Using Email-To-PDF
- Password - Encryption password must be communicated to the recipient using a channel other than email. To make it easier, the sender could use patterns. For example, a doctor's office could use the patient's social security number to encrypt the message.
Summary
We discussed three different approaches to achieve End-To-End Encryption with emails. Although every method gets the job done, the easiest way to use is Email-To-PDF, which converts the original email into a PDF document allowing the person with a password to view the message. Click here to watch a video demonstrating the ease of use inherently present in this approach.
| Created on: | May 11, 2021 |
| Last updated on: | Dec 19, 2025 |
